Did you know this about wind power?
What is wind power?
Solar energy includes wind. Wind is created by the sun’s uneven heating of the atmosphere, changes in the earth’s surface, and the earth’s rotation. Wind turbines may create power by harvesting wind flow.
How does wind energy work?
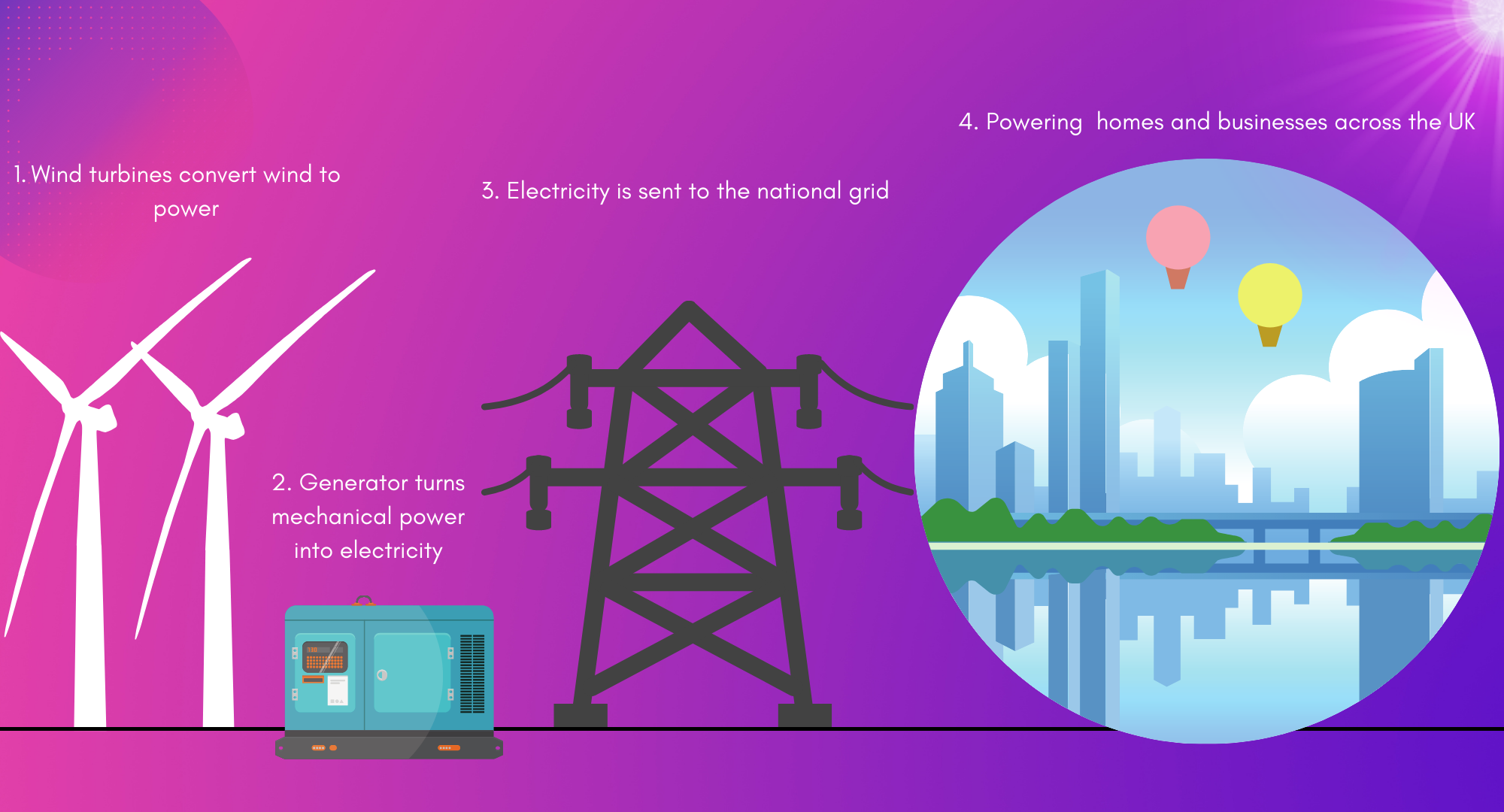
Wind turbines use the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. A generator is then utilised to turn the mechanical energy into electricity, which is ultimately used to power homes and businesses throughout the United Kingdom.
How efficient is wind power?
A wind turbine’s efficiency ranges from 30 to 45 percent, with peak wind periods reaching 50 percent. The wind would entirely decrease after passing through a wind turbine if it were 100 percent efficient.
Wind turbines in the United Kingdom generally produce electricity 70-80% of the time, making them a year-round stable source of energy.
What is a wind turbine?
A fan is the polar opposite of a wind turbine. They don’t utilise electricity to generate wind; instead, they use wind to generate power. The blades revolve when they are struck by the wind (which does not have to be forceful). This motion rotates a rotor, which spins a generator, producing kinetic energy, which is subsequently utilised to generate electricity.
How does a wind turbine work?
Wind turbines, simply described, work by being struck by the wind (which can be as little as 3-5 meteres per second). The wind then rotates a turbine’s blades around a rotor, which spins a generator, which generates energy.
If you’ve ever flown a kite or sailed a boat, you’re well aware of the wind’s strength. Of course, harnessing the wind’s energy is nothing new; windmills have been used to grind bread and power machines for hundreds of years all over the world. Wind-powered boats, on the other hand, have been around for millennia.
So there’s a lot of wind power, but how are other fatcors engaged in wind turbine electricity generation?
Choosing the best spot
They’re rarely 100 percent constant, like many other natural energy sources. Winds can weaken, blow excessively hard, or turn gusty, all of which are bad for wind turbines. So it’s critical to choose a location where the wind intensity is as predictable as possible.
The topography, which includes hills, valleys, woods, and buildings, has an impact on wind. Because all of these factors deflect and vary the available power, wind turbines should be installed in flat, high, and uninterrupted areas. That is why there are so many off-shore wind farms and why turbines may be found on the tops of hills.
Wind farms may be built in countries with flat landscapes, such as Belgium and the Netherlands, because there is little to disrupt the wind flow.
Facing the wind
Every wind turbine is equipped with a sensor that detects the strongest wind direction. The machinery that turn the top of the structure, putting the blades in the optimal position for the greatest wind, are housed in the streamlined structure behind the blade (called the nacelle). Turbines feature a brake that slows down the rotors when the wind is too powerful, preventing damage.
What is a wind farm?
To create bulk electrical power, we put our wind turbines together. The electricity is then pumped into the national utility system, where it is delivered to thousands of our customers’ homes across the United Kingdom.
The life of a wind turbine
Wind farms can be constructed far more quickly than any other sort of electricity plant. A wind farm capable of generating 50 MW of electricity may be built in as little as 6 months!
Wind turbines are designed to endure 20–25 years. During this period, some parts may need to be replaced.
